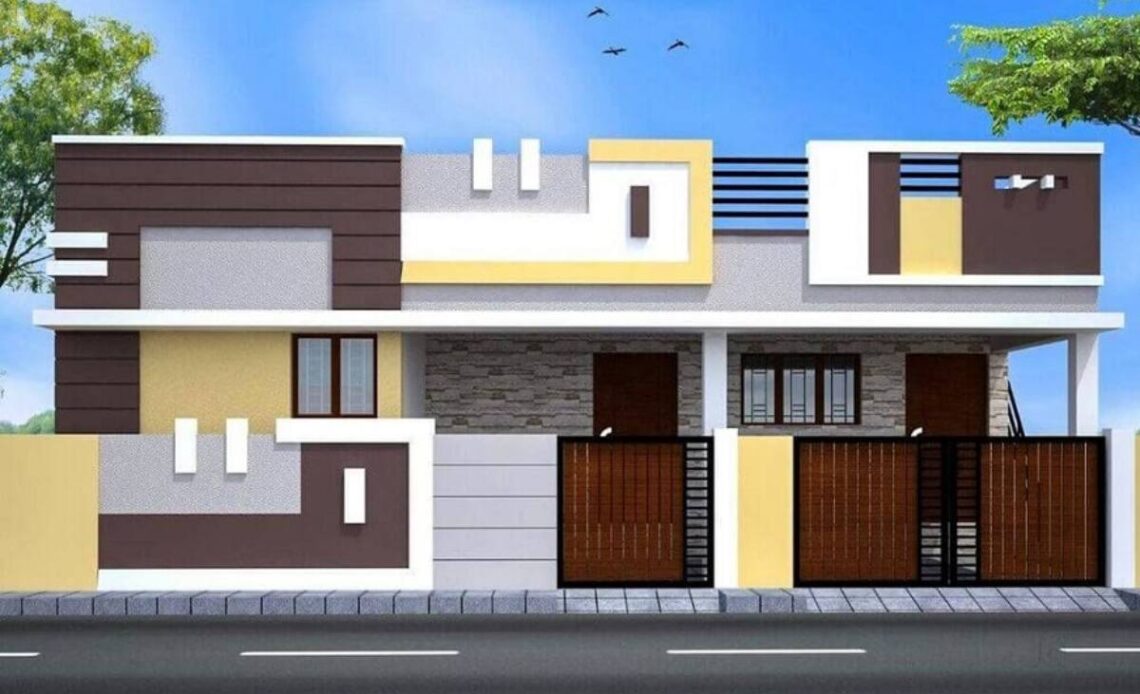
A parapet wall is a low wall that extends above the roofline of a building. Commonly found in rural architecture, especially in villages, parapet walls serve both practical and aesthetic purposes. These walls provide safety, privacy, and weather protection while enhancing the building’s appearance. In this article, we’ll explore the role of parapet wall design in village construction, key design considerations, and their benefits.
Purpose of Parapet Walls in Villages
In rural areas, parapet walls are essential for several reasons:
- Safety: Parapet walls prevent falls, especially on flat roofs, which are common in village houses. They offer protection for people using rooftops for various tasks like drying crops or storage.
- Privacy and Security: In crowded village settings, parapet walls act as barriers, providing privacy and delineating property lines between houses.
- Weather Protection: Parapets can reduce the impact of harsh winds and protect the roof from rainwater, which is especially useful in areas with heavy rainfall.
Key Design Considerations
When designing a parapet wall in a village, several factors must be considered to ensure the wall is functional, durable, and aesthetically pleasing:
- Materials: The choice of material depends on local availability and climate. Common materials in villages include:
- Stone: Durable and blends well with the environment.
- Brick: Offers strength and aesthetic appeal.
- Mud/Clay: Used in traditional designs, especially in rural areas with limited resources.
The material should be chosen for its ability to withstand local weather conditions and provide adequate insulation.
- Height: The height of a parapet wall typically ranges from 3 to 4 feet. It must be high enough to prevent falls and provide privacy but not too tall to obstruct views or light.
- Thickness: A parapet wall must be thick enough to offer structural stability but not overly bulky. A thickness of about 6 to 8 inches is common, but this can vary based on local building practices and weather conditions.
- Roof Integration: The parapet should integrate smoothly with the roof, ensuring that it does not obstruct water drainage. Proper drainage prevents water from accumulating on the roof, reducing the risk of leaks or structural damage.
- Style: While traditional parapet walls are often simple and functional, some villages feature decorative designs with carvings or patterns that reflect local culture. The style should complement the overall architecture of the home.
Benefits of parapet wall design in village Settings
- Enhanced Safety: Parapet walls protect individuals from falling off roofs, making them especially important in rural areas where roofs are used for multiple activities.
- Privacy: They help prevent unwanted visibility between neighboring houses, ensuring a higher level of privacy in crowded village settings.
- Weather Protection: Parapets protect the building from weather-related damage by preventing rainwater from spilling over the roof edges and safeguarding against wind erosion.
- Aesthetic Value: Well-designed parapet walls can add a touch of character and tradition to a building’s exterior, especially when crafted from local materials.
Conclusion
Parapet walls are a practical and aesthetic feature in village architecture. They provide safety, privacy, and weather protection while enhancing the overall look of the home. The design of parapet wall design in village should consider local materials, climate, and the specific needs of the inhabitants to ensure that they serve their intended purpose effectively.