Introduction
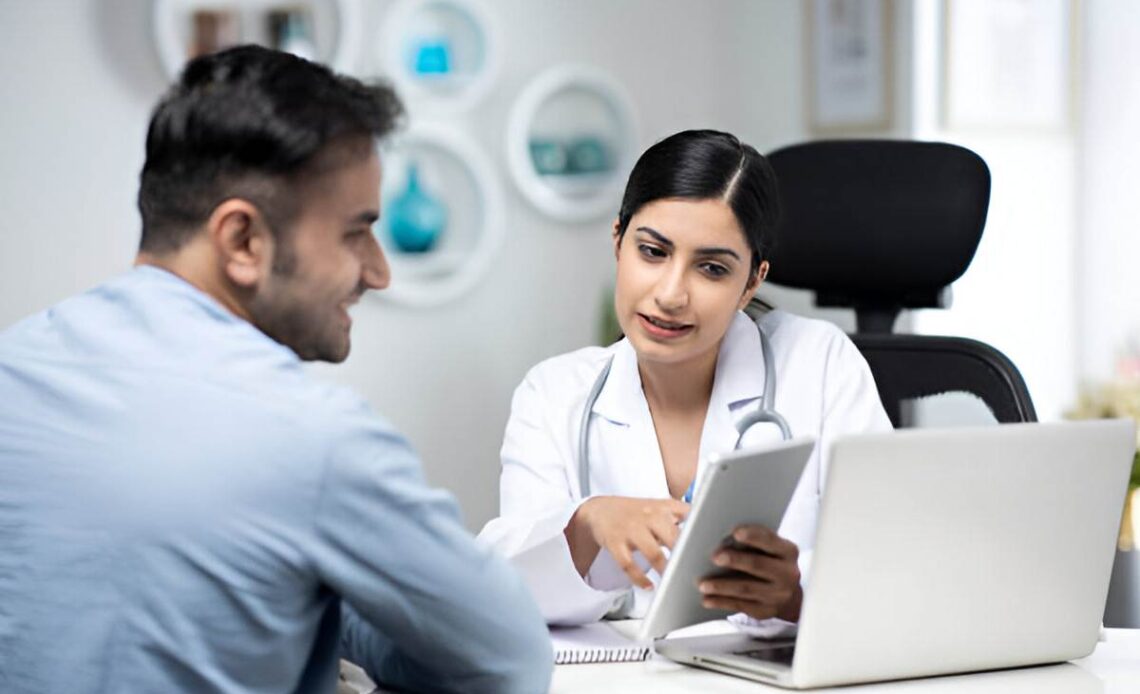
In 2024, healthcare safety remains a growing concern. A national survey found that 91% of emergency physicians had experienced workplace violence or knew a colleague who had. Additionally, the NHS in England spends £14.7 billion annually addressing harm caused by care errors, with around 820 preventable deaths each year. These numbers point to a system in urgent need of reform. This article explores how healthcare providers can improve safety for both staff and patient. It covers the use of technology, staff training, monitoring systems, safety culture, emergency preparedness, and the importance of implementing robust healthcare security systems. Each section provides practical guidance on building safer, more responsive healthcare environments.
Implementing Advanced Security Systems
To begin with, healthcare providers are turning to advanced security tools like badge-based alerts and AI-powered surveillance. For example, staff at Northeast Georgia Health System use wearable badges that enable rapid emergency communication during threats.
Moreover, deploying healthcare security systems such as real-time monitoring cameras and access controls helps detect suspicious activity and prevent unauthorized access. These systems create a safer space for both patients and staff.
Prioritizing Staff Training and Support
Next, healthcare organizations must prioritize staff training. Training sessions on conflict de-escalation, emergency procedures, and hazard identification are essential in preventing workplace incidents.
In addition, offering mental health support and creating peer support systems can reduce burnout and improve staff resilience. This holistic approach supports both safety and job satisfaction.
Enhancing Patient Monitoring and Care
Furthermore, technology-driven monitoring tools help prevent avoidable medical incidents. Wearables and remote monitoring systems allow healthcare teams to act quickly when vital signs show risk.
Simultaneously, healthcare security systems can track patient movement using advanced camera networks, helping reduce fall risks and ensuring quick response to patient emergencies.
Fostering a Culture of Safety
In parallel, a strong safety culture must be cultivated at all levels. Leaders should promote safety through regular meetings, clear protocols, and open feedback loops.
Also, involving patients and families—through initiatives like Martha’s Rule—ensures care concerns are addressed early, helping to avoid escalation and harm.
Utilizing Data for Continuous Improvement
Subsequently, healthcare systems should use safety data to drive decision-making. Tracking incident reports, safety audits, and staff feedback helps identify trends and problem areas.
Over time, analyzing this data can lead to strategic improvements in policies, tools, and staff training methods to reduce future incidents.
Collaborating with Security Experts
At the same time, collaborating with security professionals ensures that safety protocols are effective and current. These experts can evaluate risks, recommend tech upgrades, and offer specialized training.
By incorporating professional input, hospitals can maintain comprehensive healthcare security systems that adapt to evolving threats.
Ensuring Compliance with Safety Standards
Simultaneously, adherence to legal and regulatory standards is key. Institutions must comply with guidelines from bodies like OSHA or The Joint Commission to maintain licenses and minimize legal risk.
Routine audits and safety reviews also help facilities stay aligned with evolving standards and patient expectations.
Investing in Infrastructure Improvements
In addition, physical infrastructure upgrades contribute to long-term safety. Improvements such as improved lighting, secure entry points, and intuitive layouts reduce risk and improve emergency response.
During renovations, involving safety experts ensures new spaces are functional and safe for staff, patients, and visitors.
Promoting Patient Engagement in Safety
Equally important, involving patients in safety protocols enhances overall effectiveness. Educating them about hygiene, procedures, and reporting issues can prevent accidents or errors.
Feedback tools like surveys and suggestion systems also help uncover blind spots that internal audits may miss.
Preparing for Emergency Situations
Finally, every facility should have a robust emergency response plan. These plans must include scenarios for natural disasters, cyber threats, and active threats within the hospital.
Training staff through drills ensures that everyone knows their role, which reduces panic and improves coordination during real events.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are healthcare security systems and why are they important?
They include cameras, access control, and alert tools that help prevent and respond to safety threats.
How can hospitals improve staff safety without large budgets?
By focusing on basic training, internal protocols, and affordable alert systems.
What role does patient monitoring play in healthcare safety?
It enables early detection of issues and reduces the risk of accidents or emergencies.
How does leadership influence safety in healthcare settings?
Leaders set safety priorities, allocate resources, and drive accountability.
Are there compliance standards healthcare facilities must follow?
Yes, standards from OSHA, The Joint Commission, and health authorities must be met.
Conclusion
To conclude, improving safety in healthcare environments requires a coordinated, multi-layered strategy. Facilities must invest in staff training, monitoring tools, infrastructure upgrades, and professional support. Integrating modern healthcare security systems plays a critical role in preventing violence, tracking movements, and ensuring a timely response to threats. A commitment to continuous improvement and patient engagement strengthens the overall safety net for everyone involved.
Key Takeaways
- Implement advanced security systems like cameras and panic buttons.
- Train staff regularly in safety procedures and communication.
- Use wearables and AI tools to monitor patient health.
- Promote a culture of safety led by leadership and staff input.
- Collect and analyze data to refine safety protocols.
- Collaborate with security professionals for expert oversight.
- Stay compliant with healthcare safety standards.
Also Read: Quick Help When It Matters Most: Emergency Care in Cibolo